Education: Common NHL Injuries and Rehab - Bruins Player’s Examples
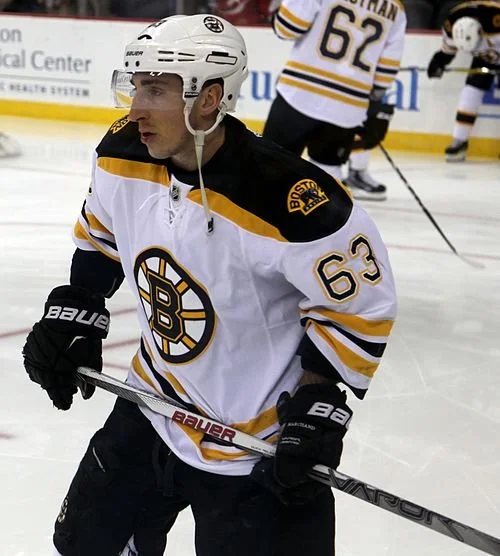
Hip Arthroscopy & Labral Repair: Example Player: Brad Marchand
What was this player’s specific injury & surgery:
5/27/2023 Double Hip Arthroscopy and Labral Repair
How did this specific injury happen:
Brad Marchand was forced to leave after a hit from Ilya Lyubushkin, a Buffalo sabres Defenseman.
In General, what does “standard PT” look like for a Double Hip Arthroscopy:
First few weeks may include: Limit standing and walking for long periods of time. Avoid deep squats and heavy lifting.
Slowly progress strength & mobility per protocol from surgeon
Slowly return to sport specific exercises & drills with help of PT (4-6+ months typical before return to sport)
How long did it take this specific player to return to the ice:
It took about 5 months for Marchand to return to the ice.
In General - how does this injury happen:
A labral hip tear happens can happen with overuse, or a traumatic injury, or an abnormality in the shape of the hip.
What is the anatomy of the hip:
It is composed of two bones
the thigh bone or femur
and the pelvis
Which is made up of three bones called: ilium, ischium & pubis
The ball of the hip joint is made by the femoral head while the socket is formed by the acetabulum.
The labrum is a thick piece of cartilage that lines the rim of the acetabulum
In General, How can a Physical Therapist help a hip injury
Conservative treatment could consist of physical therapy which can include
Soft tissue mobilization
Joint mobilizations
Modifying activities for a short time period
Targeted exercise
Stretching and mobility regimen
In General, How long does it take for someone to heal from a hip tear
It would take about 4-6 months to heal from a hip tear but the whole recovery time will take a longer period of time cause there is always a chance for re-injury.
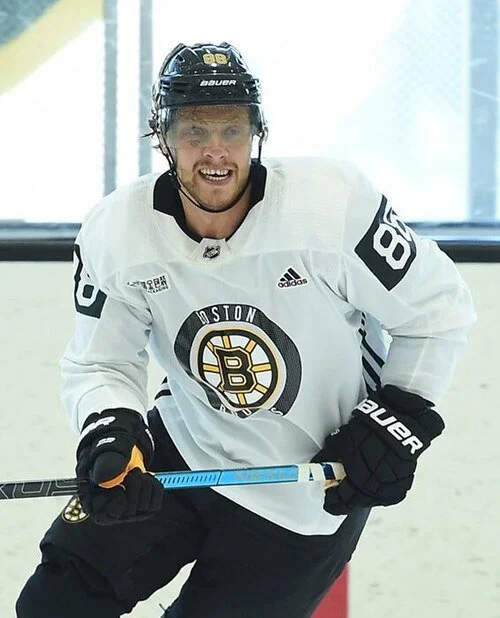
Shoulder Dislocation: Example Player: David Pastrnak
What was this players specific injury:
4/24/22 He dislocated his right shoulder
How did this specific injury happen:
He was checked into the boards by a Florida panther, which caused a shoulder injury
In General, How do you rehab a dislocated shoulder:
Immobilization with a sling
Icing initially
Activity modification
Physical Therapy
In General, What are some PT drills to help with a dislocated shoulder:
Often times rehab will include gentle passive range of motion, then active range of motion, then isometrics strengthening, then light banded strengthening.
Once strength is sufficient, exercises will be done to progress towards return to sport specific drills
How long did it take for this speicifc player to return to ice:
It took about 8-12 weeks
In General, how does this injury happen:
A strong blow to the arm by a fall, collision, or force
What is the anatomy of the shoulder:
The shoulder is made up of 3 bones, the scapula (shoulder blade), clavicle (collarbone) and humerus (upper arm bone)
2 joints in the shoulder allow it to move, the acromioclavicular joint, where the highest point of the scapula (acromion) meets the clavicle, and the glenohumeral joint.
The laburm is a ring of cartilage that deepends the shoulder socket and provides stability
The Rotator cuff and scapular muscles also provide stability
In General, How long does it take someone to heal from a dislocated shoulder:
It can a few weeks to several months to heal depending on severity
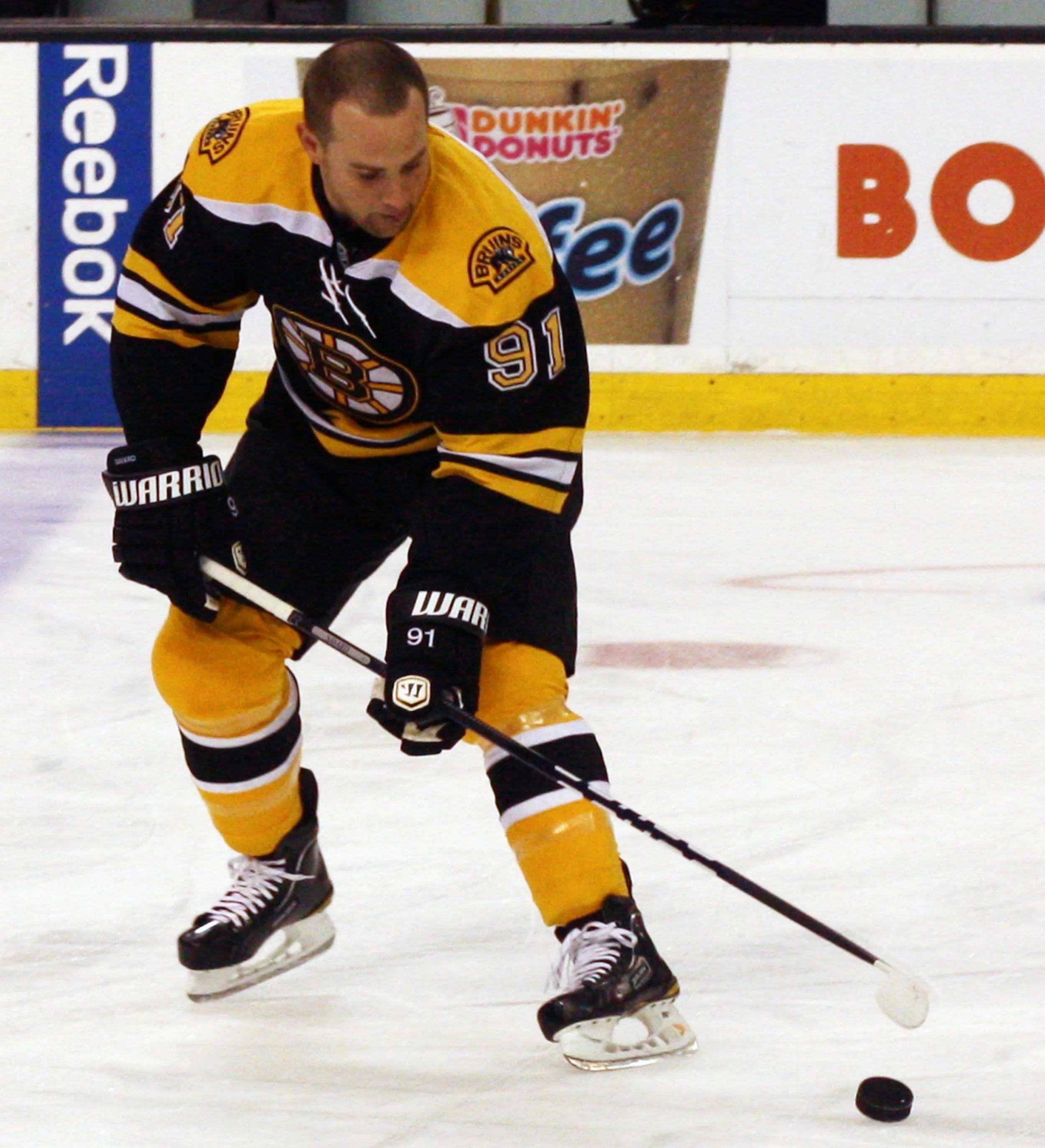
Concussions: Mark Savard
What was this player’s specific injury?
2012 Grade II Concussion
How did this specific Injury happen?
After a blindsided hit from Matt Cooke of the Pittsburg Penguins in 2010. And then suffered a second concussion in Jan 2011 by Matt Hunswick of Colorado Avalanche.
What did this specific player do to rehab it?
He mentions working with neurologists & psychologist in an article. Source: https://www.theplayerstribune.com/articles/marc-savard-bruins-hell-and-back
He saw Dr. Peter Asnis (head Boston Bruins Physician). Source: https://nesn.com/2010/03/tired-marc-savard-diagnosed-with-grade-2-concussion/
He saw “ There were consultations, sports psychologists, medication and physical therapists. "I needed to talk to somebody," Savard said. Source: https://www.espn.com/nhl/columns/story?columnist=burnside_scott&id=5900319
How long did it take (this specific player) to return to play?
Mark Savard never returned to play, it was a career ending injury.
In General, how does a concussion happen?
Concussion is a brain injury that occurs when the brain is violently shaken. The injury can happen during rapid movement changes (such as whiplash) or when the head is directly hit. This shaking or hitting of the head causes unpredictable injury to any area of the brain, resulting in immediate or delayed changes in the brain's chemistry and function. Less than 10% of concussions involve a loss of consciousness. Depending on which area of the brain suffers injury, many different temporary or permanent problems with brain function can occur. Source: https://www.choosept.com/guide/physical-therapy-guide-concussion
In General, what is the anatomy of the brain?
The Brain had 4 lobes
Frontal Lobe: Personality, thinking, problem solving
Temporal Lobe: Speech & Hearing
Pareietal Lobe: Movement, sensation, pain, taste, touch, speed & writing
Occipital Lobe: Memory, sight & smell
Cerebellum: Movement, balance, muscles
Sources: https://www.twinkl.com/teaching-wiki/brain-for-kids
In General, what are some common physical therapy exercises for this condition?
Rest
Dark room is helpful, avoiding bright lights
Quiet area, avoiding loud noises
Restoring Physical Strength
Gradual. progressive strength training exercises
Restoring Cardiovascular Strength
Gradual. progressive Zone 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 training
Bike, running, cross training machines
Restore Balance
Stability work, foam pad training, single leg drills
Reduce Headaches
Manual therapy
Neck Stretches for cervicogenic headaches
Postural related exercises
Reduce Vestibular & Vertigo Symptoms
Eye Gaze drills
Vestibular Drills
Vertigo Drills
Memory/ Cognition/ Word Finding Difficulties
Crossword Puzzles, Chess, Games
Return to Sport Skills, Coordination
Sports Specific rehab
Source: https://www.choosept.com/guide/physical-therapy-guide-concussion
In General, how long does it usually take people to heal?
Recovery from a concussion can take several weeks to several months and sometimes years, depending on many factors, including severity of the injury and the age of the person affected. Source: https://www.choosept.com/guide/physical-therapy-guide-concussion
Author: Morgan Gustafson
Editor: Matt Sweneey